
National Academic Depository (NAD) (http://nad.gov.in/)
National Academic Depository (NAD) is an initiative of Ministry of Human Resources Development, Government of India (MHRD) to facilitate digital issuance, storage, access and verification of Academic Awards issued by Academic Institutions. NAD is a Unique, Innovative and Progressive initiative under “Digital India” theme towards achieving Digital enablement of the Education Records.
NAD aspires to make the vision of Digital Academic Certificates for every Indian a reality. This touches the lives of Indian youth and empowers them with Digital, Online, Trusted, Verifiable Certificates which are accessible in a secure manner at all times. NAD promises to do away with difficulties / inefficiencies of collecting, maintaining, and presenting physical paper certificates.
Study Webs of Active Learning for Young Aspiring Minds (SWAYAM) (www.swayam.gov.in)
The Ministry of HRD, has embarked on a major and new initiative called ‘Study Webs of swyam logo final Active Learning for Young Aspiring Minds’ (SWAYAM), which will provide one integrated platform and portal for online courses, using information and communication technology (ICT) and covering all higher education subjects and skill sector courses to ensure that every student in the country has access to the best quality higher education at affordable cost.
The SWAYAM IT platform is indigenously developed that facilitates hosting of courses, taught in classrooms from 9th class till post-graduation in a number of disciplines that can be accessed by anyone, anywhere at any time. The three cardinal principles of Education Policy viz., access, equity and quality shall be achieved by providing high quality e-content to all learners in the country through SWAYAM.
Courses delivered through SWAYAM are available free of cost to the learners and are delivered by best of the teaching fraternity. Hon’ble President of India had officially launched SWAYAM, on July 9th, 2017. At present about 750 MOOCs (Massive open online courses) courses are listed on SWAYAM and about 330 MOOCs are running, wherein about 6 Lakhs (5, 92,178) students have registered for these courses.
On the auspicious occasion of “Guru Purnima” on 9th July, 2017, President of India Shri Pranab Mukherjee launched the SWAYAM.
SWAYAM PRABHA (https://www.swayamprabha.gov.in/)
Swayam Prabha is an initiative to provide 32 high quality  educational channels through DTH (Direct to Home) across the length and breadth of the country on 24X7 basis. This would enable to deliver e-education in a most cost effective manner.
educational channels through DTH (Direct to Home) across the length and breadth of the country on 24X7 basis. This would enable to deliver e-education in a most cost effective manner.
The Department of Space has allotted two Transponders of GSAT-15 for the same. The subscribers of free DTH service of Doordarshan (Free dish) would be able to view these Educational channels using the same set Top Box and TV. No additional investment would be required.
These educational programmes delivered over DTH shall also be made available at YouTube as archival data. The information  related to channel schedules; subject, archival link etc are available on SWAYAM Prabha portal (https://swayamprabha.gov.in/) which is developed by INFLIBNET Gandhinagar.
related to channel schedules; subject, archival link etc are available on SWAYAM Prabha portal (https://swayamprabha.gov.in/) which is developed by INFLIBNET Gandhinagar.
The training for untrained teachers is being conducted through Online Mode by National Institute of Open Schooling (NIOS). The online D.El.Ed. Course has already been started from 3rd October, 2017. A unique feature of this initiative is that the study material for the course prepared by NIOS in self-instructional mode,uploaded on the SWAYAM platform in four quadrants i.e. (1) Audio/Video lecture, (2) specially prepared reading material that can be downloaded/printed (3) self-assessment tests through tests and quizzes and (4) an online discussion forum for clearing the doubts.
Three courses i.e., 501, 502 and 503 have already been uploaded on the SWAYAM Portal in 4 quadrants. The D.El.Ed. programme video lectures are also broadcast on SWAYAM PRABHA (DTH Channel no. 32).
A total of 14,02,962 in-service untrained teachers from Government Aided and Private Schools have registered on the NIOS portal and 13,58,000 admissions have been confirmed so far.
Imprint India (http://imprint-india.org/)
Imprint India is an effort to direct research in the premier  institutions into areas of social relevance. Under this, 10 domains have been identified which could substantially impact the living standards of the rural areas: (1) health care technology, (2) energy security, (3) rural urban housing design, (4) Nano technology, (5) water/river system, (6) advanced materials, (7) computer science and ICT, (8) manufacturing technology, (9) advanced security and (10) environment/climate change. Each of these domains is coordinated by one IIT.
institutions into areas of social relevance. Under this, 10 domains have been identified which could substantially impact the living standards of the rural areas: (1) health care technology, (2) energy security, (3) rural urban housing design, (4) Nano technology, (5) water/river system, (6) advanced materials, (7) computer science and ICT, (8) manufacturing technology, (9) advanced security and (10) environment/climate change. Each of these domains is coordinated by one IIT.
More than 2,600 research proposals have been submitted by scientists in the priority areas of these domains. These have been examined by eminent scientists and 259 proposals for Rs. 595.89 crore have been approved for implementation. 142 research projects costing Rs. 323.17 crore with joint funding by MHRD and various participating Ministries / departments are currently under execution under IMPRINT – I. IMPRINT-II is under process for approval.
National Institutional Ranking Framework (NIRF) (www.nirfindia.org)

It was launched on 29th September 2015, ranks institutions based on objective and verifiable criteria. It has been made available separately for Engineering, Management, Pharmaceutical, Architecture, Humanities, Law and for Universities.
The first ranks were declared on 4th April 2016. More than 3,500 institutions have participated in the exercise, making it the highest participated ranking exercise in the World. The second India Rankings were released in April 2017.
Higher Education Financing Agency (HEFA)
The Cabinet considered and approved the proposal of establishment of HEFA in its meeting dated 12th September 2016. In order to give a big push for building up robust higher educational institutions, the Cabinet has approved creation of the Higher Education Financing Agency (HEFA) with Government equity of Rs. 1,000 Crore.
The creation of HEFA will enable major investments for creation of high quality infrastructure in premier educational institutions. The HEFA would be formed as an SPV within a PSU Bank/Government-owned-NBFC (Promoter). It would leverage the equity to raise up to Rs. 20,000 Crore for funding projects for infrastructure and development of world class Labs in IITs/IIMs/NITs and such other institutions.
The HEFA would finance the academic and research infrastructure projects through a 10-yr loan. The principal portion of the loan will be repaid through the ‘internal accruals’ of the institutions. The Government would service the interest portion through the regular grant assistance.
All the Centrally Funded Higher Educational Institutions would be eligible for joining as members of the HEFA. For joining as members, the Institution should agree to escrow a specific amount from their internal accruals to HEFA for a period of 10 years. This secured future flows would be securitised by the HEFA for mobilising the funds from the market. Each member institution would be eligible for a credit limit as decided by HEFA based on the amount agreed to be escrowed from the internal accruals.
The HEFA would be jointly promoted by the identified Joint Promoter, Canara Bank and the Ministry of Human Resource Development (MHRD) with an authorized capital of Rs.2,000 crore. The Government equity would be Rs.1, 000 crore.
The HEFA would also mobilize CSR funds from PSUs/Corporates, which would in turn be released for promoting research and innovation in these institutions on grant basis.
Canara Bank was identified and appointed as Joint Venture partner on 29.12.2016 for establishment of Higher Education Financing Agency (HEFA) to manage the financing agency incorporated under the Companies Act, 2013 and also registered with RBI as NBFC. An MOU was signed on 9th February, 2017 between MHRD and Canara Bank for the same. Later, Joint Venture Agreement (JVA) was also signed between MHRD and Canara Bank on 16th March, 2017.
All India Survey on Higher Education (AISHE)
 The Union Minister of Human Resource Development Prakash Javadekar released the All India Survey on Higher Education (AISHE) for the year 2016-17 in New Delhi on January 05th, 2018. On this occasion, he also launched the Survey for the year 2017-18.
The Union Minister of Human Resource Development Prakash Javadekar released the All India Survey on Higher Education (AISHE) for the year 2016-17 in New Delhi on January 05th, 2018. On this occasion, he also launched the Survey for the year 2017-18.
Findings of the survey indicate that there is an increase in overall enrollment from 27.5 million in 2010-11 to 35.7 million in 2016-17 and improvement in Gross Enrollment Ratio (GER) which is a ratio of enrollment in higher education to population in the eligible age group (18-23) years, from 19.4% in 2010-11 to 25.2 in 2016-17 which is a significant achievement.
The survey covers almost all the Higher Education institutions (HEIs) in the country including Universities, Colleges and Stand-Alone institutions. Identified nodal officers from each institution are primarily responsible for collecting and uploading the data on AISHE portal in a secured environment. It needs a lot of efforts in a survey of this scale to bring out the correct and complete picture of the system so that relevant statistics are available to the Central Government as well as State Governments, in order to devise future policies.
The survey is also unique in the sense that it is a participatory effort between State Governments, Regulatory Statutory Authorities and the Ministries of the Government of India. The Survey compiles and manages statistics directly online from respondent institutions. The main items of data collection under survey are Basic details, Programme details, Teaching & Non-Teaching Staff, Student Enrollment, Examination Result, Infrastructure, Scholarships and Foreign students etc.
The AISHE data is the main source of information for `Know Your College’ portal.
With the launching of the portal based survey, the time-lag in bringing out the reports has been reduced to bare minimum. All the institutions located in the country are requested to participate in the Survey and provide relevant data.
Prakash Javadekar expressed the hope that the GER ratio of 30% would be achieved by the year 2022. He informed that Gender Parity Index (GPI), a ratio of proportional representation of female and male, has improved from 0.86 to 0.94 to the corresponding period. To give a further boost to girl-students, the Minister announced that a supernumerary quota in IITs will be increased. Number of institutions of higher education listed on AISHE portal has also increased significantly – from 621 universities in 2010-11 to 864 in 2016-17 and from 32,974 colleges in 2010-11 to 40,026 colleges in 2016-17.
He said that the government’s vision for the higher education is based on three important aspects namely Quality, Autonomy, Research & Innovation.
Keeping in view the usefulness of data collected during the very first year, Ministry decided to make this survey an annual exercise of data collection in higher education sector. So far, survey has been completed for the years 2010-11 to 2016-17 and all the reports of AISHE are available on the website of the Ministry (www.hrd.gov.in) under the menu `Statistics’.
In the AISHE 206-17, efforts have been made for the first time to collect the details of teachers to be used in the portal `Gurujan’ specifically dedicated to teacher information. The portal is in the process of development.
Digital Infrastructure for Knowledge Sharing (DIKSHA)
 To accelerate and amplify solutions, experiments and innovations for teacher training and professional development, DIKSHA was launched on 5th September, 2017 by Vice President of India M. Venkaiah Naidu.
To accelerate and amplify solutions, experiments and innovations for teacher training and professional development, DIKSHA was launched on 5th September, 2017 by Vice President of India M. Venkaiah Naidu.
DIKSHA is for the benefit of Teachers in Schools, Teacher Educators and Student Teachers in Teacher Education Institutes (TEIs).States and TEIs have the autonomy and choice to repurpose and extend DIKSHA to suit their own needs and purposes.
National Digital Library (NDL)
 Ministry of Human Resource Development (MHRD) is establishing the National Digital Library (NDL) under the National Mission on Education through Information and Communication Technology (NMEICT) with the objective to host a national repository of existing e-content available across educational institutions in the country and e-content developed under NMEICT. IIT Kharagpur has been entrusted to host, coordinate and set-up National Digital Library (NDL) of India towards building a national asset.
Ministry of Human Resource Development (MHRD) is establishing the National Digital Library (NDL) under the National Mission on Education through Information and Communication Technology (NMEICT) with the objective to host a national repository of existing e-content available across educational institutions in the country and e-content developed under NMEICT. IIT Kharagpur has been entrusted to host, coordinate and set-up National Digital Library (NDL) of India towards building a national asset.
The objective of the project is to integrate all the existing digitized and digital contents across educational and cultural institutions/bodies to provide a single-window access to different groups of users ranging across the entire population.
NDL Portal (https: //ndl.iitkgp. ac.in) went live in February 2016 with users from selected Centrally Funded Technical Institutes (CFTIs), opened to all in February 2017 (with release of Mobile App), with daily website hits of 30,000 and User base – Registered of 17+ Lakhs.
New Education Policy (NEP)
 In view of the vastly transformed landscape of education in India in terms of coverage, content and delivery systems, a New Education Policy is being formulated after nearly 30 years.
In view of the vastly transformed landscape of education in India in terms of coverage, content and delivery systems, a New Education Policy is being formulated after nearly 30 years.
MHRD has embarked on an unprecedented collaborative, multi- stakeholder and multi-new-edu-logo.jpg pronged consultation process. The consultative process has reached out to individuals across the country through more than 2.75 lakh direct consultations while also taking online inputs. The online consultation process was undertaken on www.MyGov.in portal from 26th January, 2015 to 31st October, 2015 and nearly 29000 suggestions were received on the 33 identified themes.
Over 200 thematic national workshops were held with a youth survey by the UNESCO Mahatma Gandhi Institute of Education for Peace, Sustainable Development. With regard to School Education, 1, 10,623 villages, 3250 Blocks, 725 Urban Local Bodies from 340 districts of 19 States have uploaded their Grassroots Consultation Reports on www.MyGov.in portal.
Similarly, 2741 Blocks, 962 Urban Local Bodies from 406 districts in 20 States have done the same with regard to Higher Education. A Committee for Evolution of the New Education Policy has been constituted to examine the outcome documents, recommendations & suggestions received and formulate a draft National Education Policy as well as a Framework for Action.
Digital Board
 A number of decisions were taken at the 65 th Meeting of the Central Advisory Board of Education (CABE) was held under the Chairmanship of Union Human Resource Development Minister Prakash Javadekar.
A number of decisions were taken at the 65 th Meeting of the Central Advisory Board of Education (CABE) was held under the Chairmanship of Union Human Resource Development Minister Prakash Javadekar.
The following resolutions were adopted:-
Launch Operation Digital Board in all schools in five years. This will be undertaken jointly by Centre, State, CSR, and community. This will improve the quality of education. Students will be empowered with 360 degree information with interesting learning experience and teacher accountability will also increase.
Ensure Quality, Equity, Accessibility, Accountability and Affordability in education by pro-active action and plan.
Promote Swachh Bharat, Ek Bharat Shrestha Bharat, Padhe Bharat, Sugamya Bharat and physical education. Resolve to promote human value education, life skill education, experiential learning to bring out good human beings out of the education system.
Prakash Javadekar emphasised that education is a national agenda which empowers the individual, family, society and the nation. He highlighted some recent steps such as codification of learning outcomes, national academic depository, digital initiatives that strength education, training of 15 lakh untrained teachers, re-introduction of class X board examinations, and the status of no detention policy. He endorsed that the States requirements of additional funds is well justified.
National Testing Agency (NTA)
The Union Cabinet in its meeting held on 10.11.2017 approved creation of the National Testing Agency (NTA) as an autonomous and self-sustained premier testing organization to conduct all entrance examinations for higher education institutions in the country.
Global Initiative for Academics Network (GIAN)
The GIAN programme brings together foreign and Indian faculties to teach an academic course that provides the credit to participating students selected from the world’s leading academic institutions. Under this Scheme, foreign schemes are coming and conducting courses, out of which 802 courses have been completed. In 2017-18, a total of 156 courses have been conducted till now.
National Achievement Survey 2017-18
Touted as one of the world’s largest sample surveys of student learning achievement as hailed by MHRD Minister on November 13, 2017, around 22 lakh students from around 1,10,000 schools across 700 districts of India including rural and urban were assessed in the year 2017-18 under National Achievement Survey 2017-18. Earlier, only 4.43 lakh students were earlier tested across Classes 3, 5 and 8
Through NAS 2017-18, it will be for the first time that the teachers will have a tool to understand what exactly the child should be learning in various classes, how to teach this through activities and how to measure and ensure that children have reached the required level.
Union Minister of Ministry of Human Resource Development Prakash Javadekar hails National Achievement Survey 2017-18 as a landmark survey in the history of India. The survey which was earlier based on textbook content is now a competency based evaluation. This survey is an improvement over the previous cycles of NAS as it will be completed in the one full academic year.
It will reflect the scores of the students and will be able to suggest academic intervention in the same academic year. District wise Result will be generated within 2 months of test conduction. NAS Reporting will show if the students’ learning levels are as per the learning outcomes of a particular grade. It will also look for association of school, teacher and students’ background variables with students’ achievements while analysing the data.
Adding to this, for the first time there will be detailed district-specific report cards for all the districts in the country. This will also help agencies at the District, State, and National level to conduct achievement surveys and assess the health of the system to improve upon the policy directives.
Rashtriya Avishkar Abhiyan
 In pursuance of the focus on connecting school based knowledge to life outside the school and making learning of Science Mathematics a joyful and meaningful activity to bring focus on innovation and use of technology, the Ministry of Human Resource Development has set up the Rashtriya Avishkar Abhiyan (RAA) – a convergent framework that aims at nurturing a spirit of inquiry and creativity, love for Science and Mathematics and effective use of technology amongst children and encourage those who show an in clination and talent for these subjects to be encouraged and supported to heights of academic excellence and research.
In pursuance of the focus on connecting school based knowledge to life outside the school and making learning of Science Mathematics a joyful and meaningful activity to bring focus on innovation and use of technology, the Ministry of Human Resource Development has set up the Rashtriya Avishkar Abhiyan (RAA) – a convergent framework that aims at nurturing a spirit of inquiry and creativity, love for Science and Mathematics and effective use of technology amongst children and encourage those who show an in clination and talent for these subjects to be encouraged and supported to heights of academic excellence and research.
Rashtriya Avishkar Abhiyan will target students in the age group of 6 to 18 years and in turn the execution of RAA will span across MHRD’s schematic intervention s of Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan, Rashtriya Madhyamik Shiksha Abhiyan in the Department of School Education & Literacy and programmes and schemes of Department of Higher Education to encourage Science, Mathematics & Technology.
While emphasising the primacy of the schools and classroom transactions, the RAA aims to leverage the potential science, mathematics and technology learning in non – classroom settings. Beyond the four walls of a classroom, opportunities for science, mathematics and technology learning abound.
Accordingly, the ‘Rashtriya AvishkarAbhiyan (RAA) is planned to provide nourishing and nurturing support to and a platform for schools in a dual track approach to make Science, Mathematics and Technology exciting to children and encourage them to have an enduring interest both inside classroom and outside classroom
Uchchtar Aavishkar Abhiyaan
The scheme was launched to promote industry-specific need-based research so as to keep up the competitiveness of the Indian industry in the global market. All the IITs have been encouraged to work with the industry to identify areas where innovation is required and come up with solutions that could be brought up to the commercialization level.
Under the UAY, it is proposed to invest Rs. 250 crores every year on identified projects proposed by IITs, provided the Industry contributes 25% of the project cost. For the year 2016-17, (92) projects for Rs. 285.15 crore have been approved for implementation.
IIT Madras is the National Coordinator of the scheme. 160 proposals have been received of which industry has agreed to contribute Rs. 156 Crore, making this one of the biggest ever industry-academia partnership. These research projects are expected to result in registration of patents.
Smart India Hackathon 2017
 First time India organized Smart India with participation of more than 42,000 engineering students working on 600 problem statement to all digital solutions from 30 ministries. Second Smart India Hackathon 2018 has been announced and about one lakh engineering students are expected to participate.
First time India organized Smart India with participation of more than 42,000 engineering students working on 600 problem statement to all digital solutions from 30 ministries. Second Smart India Hackathon 2018 has been announced and about one lakh engineering students are expected to participate.
SHAGUN portal
 The Union HRD Minister Prakash Javadekar launched a dedicated web portal ‘ShaGun’ to capture and showcase innovations and progress in Elementary Education sector of India by continuous monitoring of the flagship scheme – Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA). The Minister also unveiled the ‘Toolkit for Master Trainers in Preparing Teachers for Inclusive Education for Children with Special Needs’, which has been prepared by World Bank in collaboration with Ministry of Human Resource Development.
The Union HRD Minister Prakash Javadekar launched a dedicated web portal ‘ShaGun’ to capture and showcase innovations and progress in Elementary Education sector of India by continuous monitoring of the flagship scheme – Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA). The Minister also unveiled the ‘Toolkit for Master Trainers in Preparing Teachers for Inclusive Education for Children with Special Needs’, which has been prepared by World Bank in collaboration with Ministry of Human Resource Development.
Government is also committed towards improving the ‘Quality’ of Education. HRD Ministry has undertaken massive activity of codifying the learning outcome to set assessment standards for abilities with regards to comprehension, mathematics, language and thus ensuring that “all children acquire at least the minimum levels of learning” from Class I to Class VIII under Right to Education Act, 2009.
Learning Outcomes are assessment standards indicating the expected levels of learning that children should achieve for that class. These outcomes can be used as check points to assess learning at different points of time. The learning outcomes would help teachers to understand the learning levels of children in their respective classes individually as well as collectively. Learning outcomes should be the point of reference for conducting achievement surveys. Hence it is necessary that the defined Learning Outcomes are also shared with parents and community at large. Ministry of HRD has uploaded draft document on its website in this regard to invite comments and suggestions through email address given. (feedback.lo@ciet.nic.in)
School Education Initiative

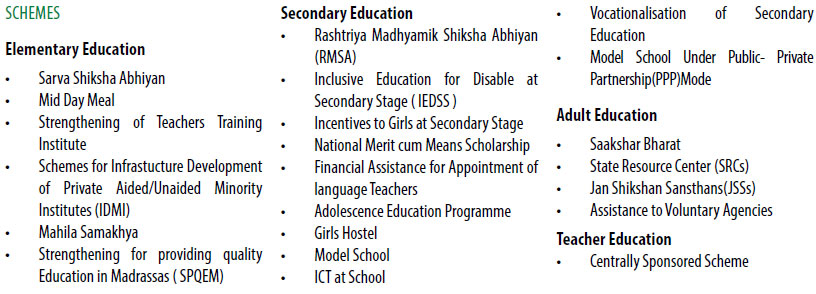
Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan (www.ssashagun.nic.in/)
 SSA has been operational since 2000-2001 to provide for a variety of interventions for universal access and retention, bridging of gender and social category gaps in elementary education and improving the quality of learning. SSA interventions include inter alia, opening of new schools and alternate schooling facilities, construction of schools and additional classrooms, toilets and drinking water, provisioning for teachers, regular teacher in service training and academic resource support, free textbooks& uniforms and support for improving learning achievement levels / outcome. With the passage of the RTE Act, changes have been incorporated into the SSA approach, strategies and norms. The changes encompass the vision and approach to elementary education, guided by the following principles :
SSA has been operational since 2000-2001 to provide for a variety of interventions for universal access and retention, bridging of gender and social category gaps in elementary education and improving the quality of learning. SSA interventions include inter alia, opening of new schools and alternate schooling facilities, construction of schools and additional classrooms, toilets and drinking water, provisioning for teachers, regular teacher in service training and academic resource support, free textbooks& uniforms and support for improving learning achievement levels / outcome. With the passage of the RTE Act, changes have been incorporated into the SSA approach, strategies and norms. The changes encompass the vision and approach to elementary education, guided by the following principles :
Holistic view of education, as interpreted in the National Curriculum Framework 2005, with implications for a systemic revamp of the entire content and process of education with significant implications for curriculum, teacher education, educational planning and management.
Equity, to mean not only equal opportunity, but also creation of conditions in which the disadvantaged sections of the society – children of SC, ST, Muslim minority, landless agricultural workers and children with special needs, etc. – can avail of the opportunity.
Access, not to be confined to ensuring that a school becomes accessible to all children within specified distance but implies an understanding of the educational needs and predicament of the traditionally excluded categories – the SC, ST and others sections of the most disadvantaged groups, the Muslim minority, girls in general, and children with special needs.
Gender concern, implying not only an effort to enable girls to keep pace with boys but to view education in the perspective spelt out in the National Policy on Education 1986 /92; i.e. a decisive intervention to bring about a basic change in the status of women.
Centrality of teacher, to motivate them to innovate and create a culture in the classroom, and beyond the classroom, that might produce an inclusive environment for children, especially for girls from oppressed and marginalised backgrounds.
Moral compulsion is imposed through the RTE Act on parents, teachers, educational administrators and other stakeholders, rather than shifting emphasis on punitive processes. Convergent and integrated system of educational management is pre-requisite for implementation of the RTE law. All states must move in that direction as speedily as feasible.
Mid-Day Meal Scheme (www.mdm.nic.in/)
 With a view to enhancing enrollment, retention and attendance and simultaneously improving nutritional levels among children, the National Programme of Nutritional Support to Primary Education (NP-NSPE) was launched as a Centrally Sponsored Scheme on 15th August 1995.
With a view to enhancing enrollment, retention and attendance and simultaneously improving nutritional levels among children, the National Programme of Nutritional Support to Primary Education (NP-NSPE) was launched as a Centrally Sponsored Scheme on 15th August 1995.
In 2001 MDMS became a cooked Mid Day Meal Scheme under which every child in every Government and Government aided primary school was to be served a prepared Mid Day Meal with a minimum content of 300 calories of energy and 8 to12 gram protein per day for a minimum of 200 days. The Scheme was further extended in 2002 to cover not only children studying in Government, Government aided and local body schools, but also children studying in Education Guarantee Scheme (EGS) and Alternative & Innovative Education (AIE) centres.
In September 2004 the Scheme was revised to provide for Central Assistance for Cooking cost @ Re 1 per child per school day to cover cost of pulses, vegetables cooking oil, condiments, fuel and wages and remuneration payable to personnel or amount payable to agency responsible for cooking. Transport subsidy was also raised from the earlier maximum of Rs 50 per quintal to Rs. 100 per quintal for special category states and Rs 75 per quintal for other states. Central assistance was provided for the first time for management, monitoring and evaluation of the scheme @ 2% of the cost of foodgrains, transport subsidy and cooking assistance. A provision for serving mid day meal during summer vacation in drought affected areas was also made.
In July 2006 the Scheme was further revised to enhance the cooking cost to Rs 1.80 per child/school day for States in the North Eastern Region and Rs 1.50 per child / school day for other States and UTs. The nutritional norm was revised to 450 Calories and 12 gram of protein. In order to facilitate construction of kitchen-cum-store and procurement of kitchen devices in schools provision for Central assistance @ Rs. 60,000 per unit and @ Rs. 5,000 per school in phased manner were made.
In October 2007, the Scheme was extended to cover children of upper primary classes (i.e. class VI to VIII) studying in 3,479 Educationally Backwards Blocks (EBBs) and the name of the Scheme was changed from ‘National Programme of Nutritional Support to Primary Education’ to ‘National Programme of Mid Day Meal in Schools’. The nutritional norm for upper primary stage was fixed at 700 Calories and 20 grams of protein. The Scheme was extended to all areas across the country from 1.4.2008.
The Scheme was further revised in April 2008 to extend the scheme to recognized as well as unrecognized Madarsas / Maqtabs supported under SSA .
Strengthening of Teacher’s Training Institutes
Originally, the Government launched the Scheme of Restructuring and Re-organisation of Teacher Education in 1987. The aim of this scheme was to create a sound institutional infrastructure for pre-service and in-service training of elementary and secondary school teachers and for provision of academic resource support to elementary and secondary schools.
The scheme had the following components :
Setting up of District Institutes of Education and Training (DIETs)
Strengthening of Secondary Teachers Education Institutions into Colleges of Teacher Education (CTEs) and Institutes of
Advanced Study in Education (IASEs)
Strengthening of State Councils of Educational Research and Training (SCERTs)
This scheme was revised under the Xth Plan, with the following main objectives :
Speedy completion of DIET/CTE/IASE/SCERT projects, which have been sanctioned but not completed up to the end of the IX Plan period
Making DIETs, CTEs, IASEs sanctioned (and SCERTs strengthened) upto the IX Plan period, optimally functional and operational
Sanction and implementation of fresh DIET/CTE/IASE/SCERT projects to the extent necessary
Improvement in the quality of programmes being undertaken by DIETs, etc. – especially those of pre-service and in-service training, so as to enable them to effectively play their nodal role of improving quality of elementary and secondary education in their respective jurisdiction, as measured in terms of levels of learner achievement
Madhyamik Shiksha Abhiyan (www.rmsaindia.gov.in/en)
 This scheme was launched in March, 2009 with the objective to enhance access to secondary education and to improve its quality. The implementation of the scheme started from 2009-10. It is envisaged to achieve an enrollment rate of 75% from 52.26% in 2005-06 at secondary stage of implementation of the scheme by providing a secondary school within a reasonable distance of any habitation. The other objectives include improving quality of education imparted at secondary level through making all secondary schools conform to prescribed norms, removing gender, socio-economic and disability barriers, providing universal access to secondary level education by 2017, i.e., by the end of 12th Five Year Plan and achieving universal retention by 2020.
This scheme was launched in March, 2009 with the objective to enhance access to secondary education and to improve its quality. The implementation of the scheme started from 2009-10. It is envisaged to achieve an enrollment rate of 75% from 52.26% in 2005-06 at secondary stage of implementation of the scheme by providing a secondary school within a reasonable distance of any habitation. The other objectives include improving quality of education imparted at secondary level through making all secondary schools conform to prescribed norms, removing gender, socio-economic and disability barriers, providing universal access to secondary level education by 2017, i.e., by the end of 12th Five Year Plan and achieving universal retention by 2020.
Important physical facilities provided under the scheme are:
(i) Additional class rooms, (ii) Laboratories, (iii) Libraries, (iv) Art and crafts room, (v) Toilet blocks, (vi) Drinking water provisions and (vii) Residential Hostels for Teachers in remote areas.
Important quality interventions provided under the scheme are:
(i) appointment of additional teachers to reduce PTR to 30:1, (ii) focus on Science, Math and English education, (iii) In-service training of teachers, (iv) science laboratories, (v) ICT enabled education, (vi) curriculum reforms; and (vii) teaching learning reforms.
Important equity interventions provided in the scheme are:
(i) special focus in micro planning (ii) preference to Ashram schools for upgradation (iii) preference to areas with concentration of SC/ST/Minority for opening of schools (iv) special enrollment drive for the weaker section (v) more female teachers in schools; and (vi) separate toilet blocks for girls.
The scheme is being implemented by the State government societies established for implementation of the scheme. The central share is released to the implementing agency directly. The applicable State share is also released to the implementing agency by the respective State Governments.
School GIS (www.schoolgis.nic.in/)
Web Based School GIS application is an initiative of the Department of School Education and Literacy, Ministry of Human Resources Department, Government of India for seamless visualization of school locations across the country.
Geographic location of schools collected by the various School Education Departments of the states has been collated and mapped on GIS Platform established by National Informatics Centre. Further, these school locations have been interlinked with the school report cards based on U-DISE database, developed and hosted by National University of Educational Planning and Administration.
In this application, base map services like street maps, and high resolution satellite images are available for better understanding of the topography/ terrain of the location. This web service application comprises of administrative boundaries up to village level and location information up to habitation level along with basic GIS functionalities and measurement tools which will help to improve the quality of planning and better utilization of resources available under the Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA) and Rashtriya Madhyamik Shiksha Abhiyan (RMSA)
Rashtriya Uchchatar Shiksha Abhiyan (RUSA)
 Rashtriya Uchchatar Shiksha Abhiyan (RUSA) is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme (CSS), launched in 2013 aims at providing strategic funding to eligible state higher educational institutions. The central funding (in the ratio of 60:40 for general category States, 90:10 for special category states and 100% for union territories) would be norm based and outcome dependent. The funding would flow from the central ministry through the state governments/union territories to the State Higher Education Councils before reaching the identified institutions. The funding to states would be made on the basis of critical appraisal of State Higher Education Plans, which would describe each state’s strategy to address issues of equity, access and excellence in higher education.
Rashtriya Uchchatar Shiksha Abhiyan (RUSA) is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme (CSS), launched in 2013 aims at providing strategic funding to eligible state higher educational institutions. The central funding (in the ratio of 60:40 for general category States, 90:10 for special category states and 100% for union territories) would be norm based and outcome dependent. The funding would flow from the central ministry through the state governments/union territories to the State Higher Education Councils before reaching the identified institutions. The funding to states would be made on the basis of critical appraisal of State Higher Education Plans, which would describe each state’s strategy to address issues of equity, access and excellence in higher education.
Objectives
The salient objectives of RUSA are to;
Improve the overall quality of state institutions by ensuring conformity to prescribed norms and standards and adopt accreditation as a mandatory quality assurance framework.
Usher transformative reforms in the state higher education system by creating a facilitating institutional structure for planning and monitoring at the state level, promoting autonomy in State Universities and improving governance in institutions.
Ensure reforms in the affiliation, academic and examination systems.
Ensure adequate availability of quality faculty in all higher educational institutions and ensure capacity building at all levels of employment.
Create an enabling atmosphere in the higher educational institutions to devote themselves to research and innovations.
Expand the institutional base by creating additional capacity in existing institutions and establishing new institutions, in order to achieve enrollment targets.
Correct regional imbalances in access to higher education by setting up institutions in unserved & underserved areas.
Improve equity in higher education by providing adequate opportunities of higher education to SC/STs and socially and educationally backward classes; promote inclusion of women, minorities, and differently abled persons.
The National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT)
The National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT) is an autonomous organisation set up in 1961 by the Government of India to assist and advise the Central and State Governments on policies and programmes for qualitative improvement in school education. The major objectives of NCERT and its constituent units are to: undertake, promote and coordinate research in areas related to school education; prepare and publish model textbooks, supplementary material, newsletters, journals and develops educational kits, multimedia digital materials, etc. organise pre-service and in-service training of teachers; develop and disseminate innovative educational techniques and practices;collaborate and network with state educational departments, universities, NGOs and other educational institutions; act as a clearing house for ideas and information in matters related to school education; and act as a nodal agency for achieving the goals of Universalisation of Elementary Education. In addition to research, development, training, extension, publication and dissemination activities, NCERT is an implementation agency for bilateral cultural exchange programmes with other countries in the field of school education. The NCERT also interacts and works in collaboration with the international organisations, visiting foreign delegations and offers various training facilities to educational personnel from developing countries.
Other Initiatives
Improving Gender Balance in IITs: For improving Gender Balance in IITs, the IIT Council in its 51st meeting held on 28.04.2017, on the basis of the recommendations of a JAB Sub Committee, and decided to increase female enrolment in B.Tech. programmes of IITs from the current 8% to 14% in 2018-19, 17% in 2019-20 and 20% in 2020-21 by creating supernumerary seats.
Several welfare measures viz. Anti-Ragging Cell, Anti-discrimination Cell, Gender Sensitization Cell, Internal Complaints Committee for prevention of Sexual Harassment & Barrier Free access for specially abled students in all places have been introduced.
Six new IITs at Jammu, Bhilai, Goa, Dharwad, Tirupati and Palakkad were established and operationalized at a total cost of Rs.1411 crore.
The proposal for construction of permanent campuses of these IITs was approved by the Union Cabinet in November, 2017 at a total cost of Rs.7002.42 crore for Phase-A.
Wi-Fi under implementation in 38 Central Universities.
University Grants Commission (Open and Distance Learning) Regulations, 2017 have been recently notified in the month of June, 2017 keeping in view the urgent need of appropriate regulations for monitoring of higher education through the open and distance mode. The open and distance learning system in India has emerged as an important mode for providing education to diverse sections of society. These regulations provide clear directions and instructions for HEIs proposing to offer UG and PG courses through the ODL mode, along with the mechanism of approvals, assessment and monitoring.
UGC (Institutions of Eminence Deemed to be Universities) Regulations, 2017 have been notified to create a distinct category of Deemed to be Universities, called Institutions of Eminence Deemed to be Universities, which would be regulated differently from other Deemed to be Universities so as to evolve into Institutions of world class in reasonable time period. Also, in order to assist Indian Higher Education Institutions to get a rank within the top 100 in globally renowned rankings, UGC has invited applications under the Institutions of eminence scheme wherein 10 institutions from the government and 10 institutions from the private sector are to be selected. Government Institutions will get financial assistance of 1000 crores over a period of five years in addition to the grant already being received.
The institutions selected from the private sector will have complete autonomy to promote innovation and creativity expected to result in producing competent graduates for the development of the country.


























